Surgeons use the word “arthroplasty” to mean replacement. The word “total” means that both the ball and socket part of the hip are replaced. Therefore, “total hip arthroplasty” means a total hip replacement.
When should hip replacement be considered?
The ideal time for surgery is when other measures — such as medicines, exercise, weight loss and alternative therapies — no longer work. If hip pain causes a limp, affects your lifestyle, interferes with work or recreation and hurts your body image, then surgery is a reasonable option.
Total Hip Replacement
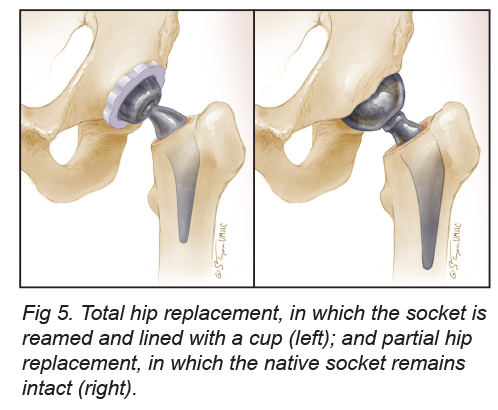
Hip surgeries are performed for patients with hip arthritis, a condition where the blood flow into the hip has been damaged (avascular necrosis), or some hip fractures. Total hip replacement involves replacing both sides of the hip joint. Some less active patients with a hip fracture affecting only the thigh bone (femoral) side of the hip joint might only have the thigh bone side of the hip joint replaced (hemi-arthroplasty or partial hip replacement).
Total hip replacement surgery involves the removal of damaged bone and cartilage from the hip joint. The damaged parts of your hip joint are removed with parts placed into your pelvis (hip socket) and femur (thigh bone).
Less invasive hip surgery
All of our surgeons perform surgery using a smaller incision at the skin level with less cutting of the muscle tissues around the hip when compared to traditional hip replacement performed 15-30 years ago. The size of the incision will change depending on your physical size and what is needed to put your hip parts in as accurately as possible. Incisions are most commonly closed with sutures placed below the skin that will dissolve on their own over the course of a few weeks.
What are the advantages of hip replacement?
A key advantage is its longevity and track record. The technology used in modern hip replacements is safe and well proven in millions of patients. The nuances, complications, surgical techniques and outcomes of this operation have been thoroughly investigated. A properly performed hip replacement should last a lifetime — this is significant, because no one wants repeat surgery.
Different bearing surfaces can be used in hip replacement. This is because there is more latitude in the engineering design of hip replacement components. In hip replacement, once the metal shell and the femoral stem are implanted, the surgeon and patient have a choice of bearing, including metal-metal, metal-plastic, metal-ceramic, ceramic-plastic and ceramic-ceramic.
Hip Surgery Technique
What is a surgical approach?
The anatomic pathway used to reach the bones of the hip joint is also referred to as the surgical approach. Each surgical approach is a different technique to gain access to the joint itself and expose the anatomy for a hip replacement.
Minimally invasive posterior hip replacement
The minimally invasive posterior hip replacement is done through a space behind the thigh bone. It leaves the major power muscles for the hip attached. Two or three small muscles are released get access to the hip. These tendons are repaired back after the surgery.
Direct superior hip replacement
With a direct superior hip replacement approach, you lie on your side, and a 4- to 6-inch incision is made in a similar location as is used for the posterior replacement, but the approach into the hip joint occurs above the short tendons. With a direct superior approach, the surgeon replaces the hip joint without cutting through the long tendon known as the IT band that runs along the side of your hip. This may help with early recovery after surgery.
Direct anterior hip replacement
With a direct anterior hip replacement, our surgeons make a 4- to 6-inch incision at the front of the hip. The surgery is performed between the muscles and tendons on the front of the hip. This allows a slightly faster recovery for many patients.


